Motor Neuron Disease (MND) Symptoms
Mnd symptoms – Motor neuron disease (MND) is a progressive neurological condition that affects the motor neurons, the cells that control voluntary muscle movement. The most common type of MND is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease.
The symptoms of MND can vary depending on the type of the disease and the individual, but the most common symptoms include:
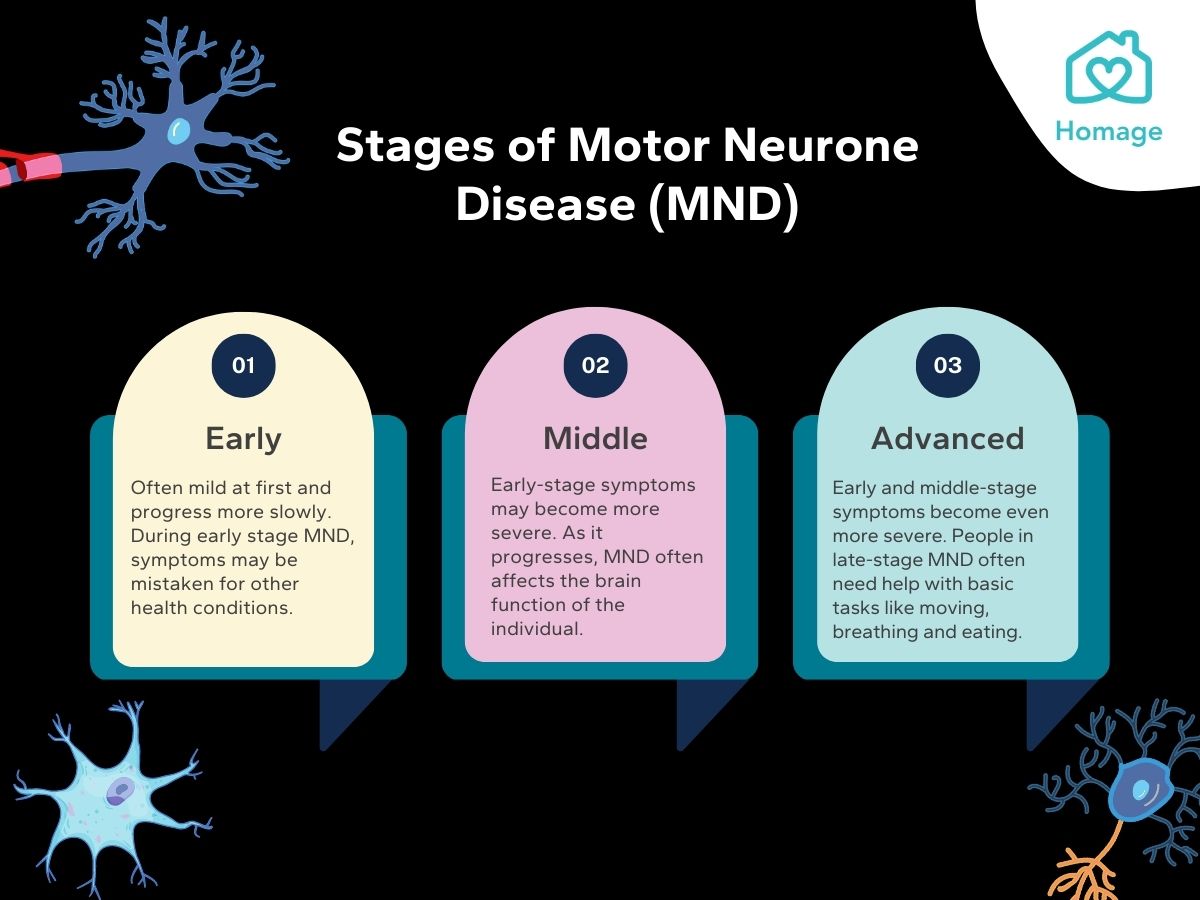
Early-Stage Symptoms
In the early stages of MND, symptoms may be mild and easily overlooked. These may include:
- Muscle weakness in the arms, legs, or face
- Twitching or cramping in the muscles
- Difficulty walking or running
- Slurred speech
- Difficulty swallowing
Late-Stage Symptoms
As MND progresses, the symptoms become more severe and debilitating. These may include:
- Paralysis of the arms, legs, and face
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty speaking
- Difficulty swallowing
- Loss of cognitive function
Impact of Symptoms on Daily Life
The symptoms of MND can have a significant impact on daily life. People with MND may experience difficulty with simple tasks such as eating, dressing, and walking. They may also experience social isolation and depression.
Differential Diagnosis of MND Symptoms

Accurate diagnosis of Motor Neuron Disease (MND) is crucial due to its progressive and often fatal nature. Other conditions can mimic MND symptoms, making differential diagnosis essential to ensure appropriate treatment and prognosis.
Conditions with similar symptoms include:
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): A genetic disorder affecting motor neurons in the spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT): A group of inherited disorders affecting peripheral nerves, causing progressive weakness and sensory loss in the hands and feet.
- Myasthenia Gravis (MG): An autoimmune disorder that weakens muscles due to impaired nerve-muscle communication.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): A progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting both upper and lower motor neurons, causing muscle weakness, spasticity, and speech difficulties.
Differential diagnosis involves a thorough clinical examination, detailed patient history, and specialized tests such as electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies. Accurate diagnosis allows for proper disease management, genetic counseling, and support for patients and their families.
Comparative Table of MND Symptoms and Other Conditions
The following table summarizes the key symptoms of MND and compares them with similar symptoms in other conditions:
| Symptom | MND | SMA | CMT | MG | ALS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle weakness | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Muscle atrophy | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Fasciculations | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Dysphagia | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Dysarthria | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Spasticity | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Sensory loss | No | No | Yes | No | No |
Note: This table provides a general overview, and specific symptoms may vary depending on the individual case and disease progression.
Management and Treatment of MND Symptoms
The management and treatment of Motor Neuron Disease (MND) symptoms aim to alleviate discomfort, improve quality of life, and prolong survival. There is currently no cure for MND, but various approaches can help manage the symptoms.
Medications
Medications can be used to relieve specific symptoms of MND. These include:
- Riluzole: Slows disease progression.
- Baclofen: Reduces muscle spasms.
- Tizanidine: Relaxes muscles.
- Amantadine: Improves muscle function.
- Antidepressants: Manages mood and anxiety.
Therapies
Therapies can also help manage MND symptoms. These include:
- Physical therapy: Improves mobility and range of motion.
- Occupational therapy: Assists with daily activities.
- Speech therapy: Helps with communication.
- Respiratory therapy: Supports breathing.
- Nutritional therapy: Ensures adequate nutrition.
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on providing comfort and support to individuals with MND. It involves managing pain, controlling symptoms, and providing emotional and spiritual support. Palliative care can help improve quality of life and well-being.